|
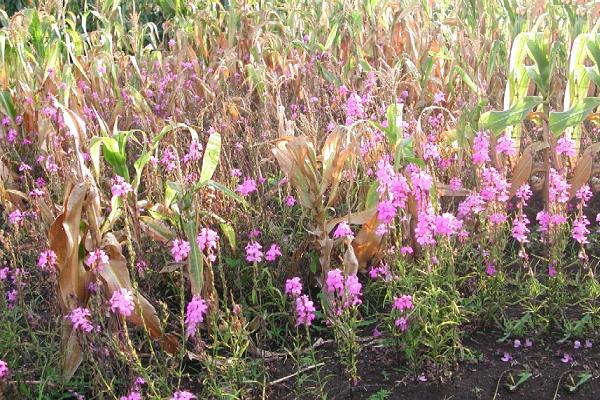
A platform technology for improving livelihoods of resource poor farmers in sub-Saharan Africa Africa faces increasingly serious problems in its ability to feed its rapidly growing population, resulting in high hunger and poverty incidences. Growth in agricultural productivity is essential to reduce hunger and poverty and ensure food security. Agricultural growth can be achieved by reducing incidence of the major constraints to productivity such as pests, weeds and degraded soils. These constraints are responsible for the continent’s crop productivity being the lowest in the world (around 1t/ha compared with 2.4t/ha in South Asia, 3.2t/ha in Latin America and 4.5t/ha in East Asia and Pacific), and cause high levels of hunger, malnutrition and poverty. More..... Stemborers, parasitic striga weeds and poor soil fertility are the three main constraints to efficient production of cereals in SSA. Losses caused by stemborers can reach as high as 80% in some areas and an average of about 15-40% in others. Losses attributed to striga weeds on the other hand range between 30 and 100% in most areas, and are often exacerbated by the low soil fertility prevalent in the region. The soils are highly degraded due to continuous cropping with limited or no external inputs to improve soil fertility. When the two pests occur together, farmers often lose their entire crop. Crop losses caused by stemborers and striga weeds amount to about US $ 7 billion annually, affecting mostly the resource poor subsistence farmers.
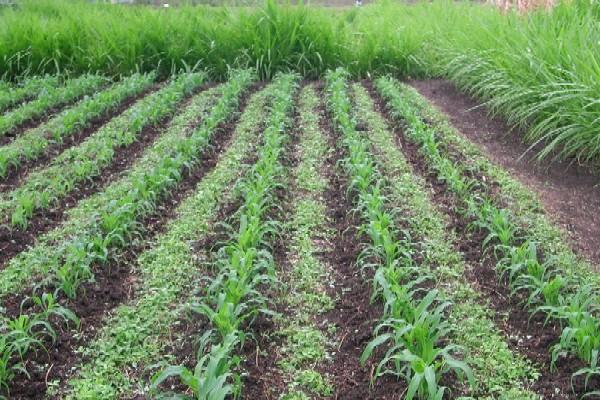
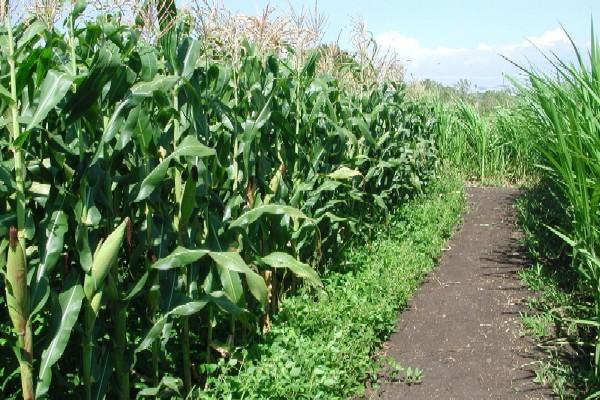
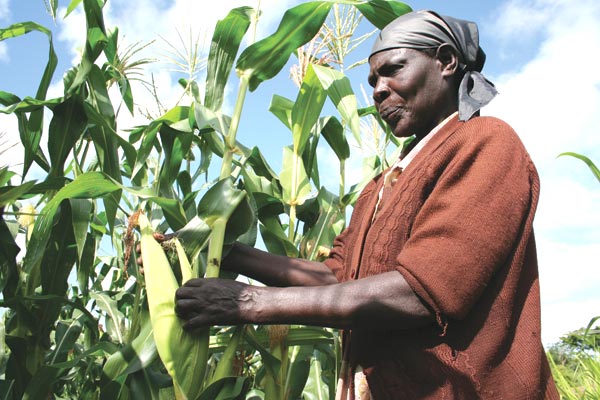
A conservation agricultural approach known as `Push-Pull' technology has been developed for integrated management of stemborers, striga weed and soil fertility. Push-Pull was developed by scientists at the International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology (icipe), in Kenya and Rothamsted Research, in the United Kingdom, in collaboration with other national partners. The technology is appropriate and economical to the resource-poor smallholder farmers in the region as it is based on locally available plants, not expensive external inputs, and fits well with traditional mixed cropping systems in Africa. To date it has been adopted by over 350,298 smallholder farmers in Africa where maize yields have increased from about 1 t/ha to 3.5 t/ha, achieved with minimal inputs. More..... Our Goal
“To end hunger and poverty for 10 million people by extending Push-Pull technology to 1 million households in sub-Saharan Africa by 2030”, Zeyaur Khan, Coordinator, Push-Pull Programme
TWAS Prize in Agriculture
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan, Principal Scientist & Programme Leader; Coordinator, Push-Pull Programme, was announced as a co-winner of the TWAS Prize .....More....
Distinguished Research Fellow
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan designated as icipe's first Thomas Odhiambo Distinguised Research Fellow.....More....
Partners
Push-Pull On Swiss TV
|
|
|
|
|










 Research Partners
Research Partners